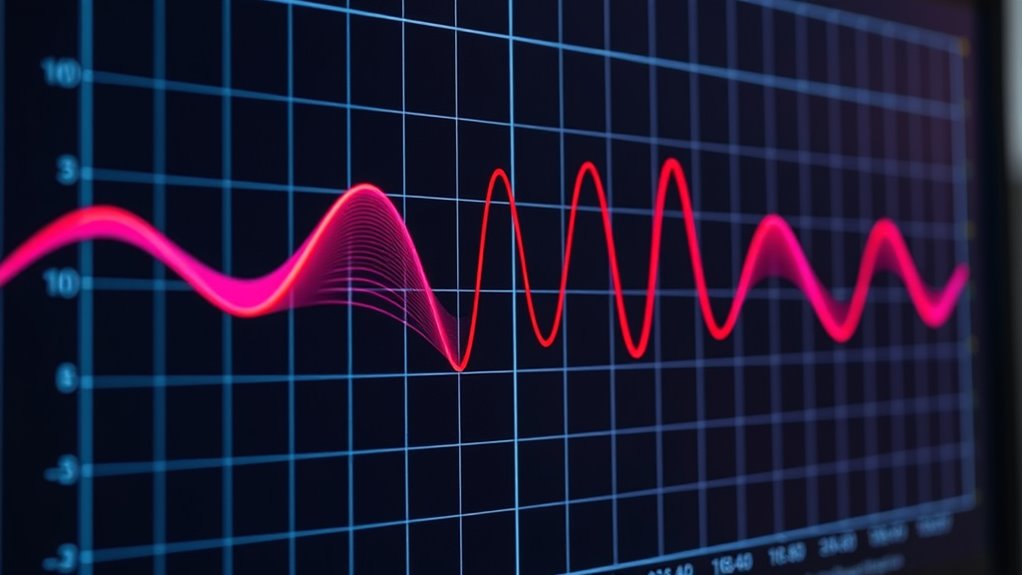
When interpreting guiding graphs, focus on the RMS error to gauge how well your robot follows the target path; a rising RMS indicates drifting, while stable low error shows accuracy. Watch for oscillations—repetitive fluctuations suggest control instability or sensor noise. If you see high error with little fluctuation, calibration might be needed. Noticing these patterns helps you identify issues quickly and improve your system’s performance—continue exploring to master effective troubleshooting techniques.
Key Takeaways
- RMS error indicates how much the robot deviates from its intended trajectory; higher values suggest greater drift.
- Oscillation patterns show repetitive fluctuations, signaling control instability or over-aggressive tuning.
- Consistent high RMS error suggests sensor calibration issues needing correction.
- Prominent oscillations point to the need for adjusting control parameters or filtering sensor noise.
- Regular graph analysis helps diagnose issues early, guiding calibration and control improvements for better navigation stability.

Guiding graphs are powerful tools that help you visualize data and understand trends quickly. When working with robotic navigation, these graphs become essential for evaluating how well your robot is following a planned path or maintaining its position. Two critical aspects to interpret on guiding graphs are RMS error and oscillation, as they reveal how accurately your robot is navigating and whether it’s experiencing instability. Recognizing these patterns enables you to troubleshoot issues like sensor calibration errors or control adjustments needed to improve performance.
RMS error, or root mean square error, provides a quantitative measure of how far your robot deviates from the desired trajectory over time. When you observe a rising RMS error on your guiding graph, it indicates that your robot is drifting away from its target. This could stem from incorrect sensor calibration, where sensors like encoders or inertial measurement units (IMUs) aren’t providing accurate data, leading to flawed navigation calculations. By analyzing the RMS error trend, you can determine whether your calibration procedures are effective or if adjustments are necessary. Consistently high RMS errors suggest that your sensors might need recalibration to enhance accuracy, which improves your robot’s ability to follow commands precisely.
High RMS error indicates drift; recalibrate sensors like encoders and IMUs for better navigation accuracy.
Oscillation, on the other hand, appears as repetitive fluctuations around a central value on the graph. If you notice your robot’s path swinging back and forth, it’s likely experiencing oscillations. These are often caused by over-aggressive control algorithms or delays in sensor feedback, which can amplify small errors into larger swings. In robotic navigation, oscillations can also hint at issues with sensor calibration, especially if sensors are providing noisy or inconsistent data. When sensors aren’t calibrated correctly, the robot’s control system might overreact to false signals, causing it to oscillate. To mitigate this, you should fine-tune your sensor calibration and control parameters, ensuring smoother, more stable movement.
Interpreting these graph patterns allows you to take targeted actions. For instance, if RMS error is high but stable, focus on improving sensor calibration to reduce drift. If oscillations are prominent, consider adjusting your control gains or refining sensor filtering techniques. In robotic navigation, keeping sensors calibrated is vital for minimizing errors and stabilizing the robot’s path. Regularly reviewing your guiding graphs helps you identify issues early and implement necessary adjustments, making your robot’s navigation more reliable and efficient. Remember, these visual cues are invaluable for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring your robotic system functions smoothly over time. Proper calibration practices are essential for the accuracy and stability of your navigation system.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do RMS Error Values Compare Across Different Types of Graphs?
When comparing RMS error values across different types of graphs, you need to ensure comparison metrics and graph normalization. RMS error helps you gauge the accuracy of your data representation, but differences in scale or units can skew results. Normalizing graphs ensures fair comparisons, so you can accurately assess which graph type offers better precision, regardless of their original scales. This process makes your comparisons more meaningful and reliable.
What Are Common Causes of Oscillation in Guiding Graphs?
You’ll notice oscillation often occurs when mount tracking missteps or sensor calibration slips. Sudden shifts or slight misalignments can cause the guiding graph to bounce back and forth. Poor calibration or unstable mount setups lead to persistent pulsations. To prevent this, regularly calibrate sensors and guarantee mount stability. Consistent care keeps guiding smooth, minimizes oscillation, and produces pristine, pinpoint images you’ll love capturing.
Can RMS Error Be Minimized Without Increasing Oscillations?
Yes, you can minimize RMS error without increasing oscillations by focusing on optical stability and proper guiding calibration. By fine-tuning your guiding system and ensuring the mount stays stable, you reduce the need for aggressive corrections that cause oscillations. Implementing more precise calibration helps your guiding algorithm respond smoothly, lowering RMS error while maintaining steady tracking. This balance improves overall image quality without introducing unwanted oscillations.
How Does Guide Star Brightness Affect RMS Error Readings?
Guide star brightness directly impacts rms error sensitivity; brighter stars reduce rms error readings because they provide clearer, more stable signals for the guiding system. When the guide star is dim, the system becomes more sensitive to noise, increasing rms error. You should select a sufficiently bright guide star to improve measurement accuracy, minimizing rms error without overly risking oscillations, which can occur if the system overcompensates for weak signals.
Are There Software Tools That Automatically Interpret Guiding Graph Data?
Yes, there are software tools that automatically interpret guiding graph data. Tools like PHD2 and Stellarmonitor offer automated analysis, helping you compare different software for your needs. These programs analyze RMS error and oscillation patterns to optimize guiding performance. By using software comparison, you can choose the best tool for your setup, ensuring accurate, real-time guidance without needing manual interpretation of graphs.
Conclusion
By understanding RMS error and oscillation in guiding graphs, you can better assess your control system’s performance. For example, if your robot’s movement shows high oscillation despite low RMS error, you know to tune your controller for smoother action. Recognizing these patterns helps you make informed adjustments, ensuring stability and precision. Ultimately, interpreting these graphs allows you to optimize your system’s response, leading to more reliable and efficient operation in real-world applications.